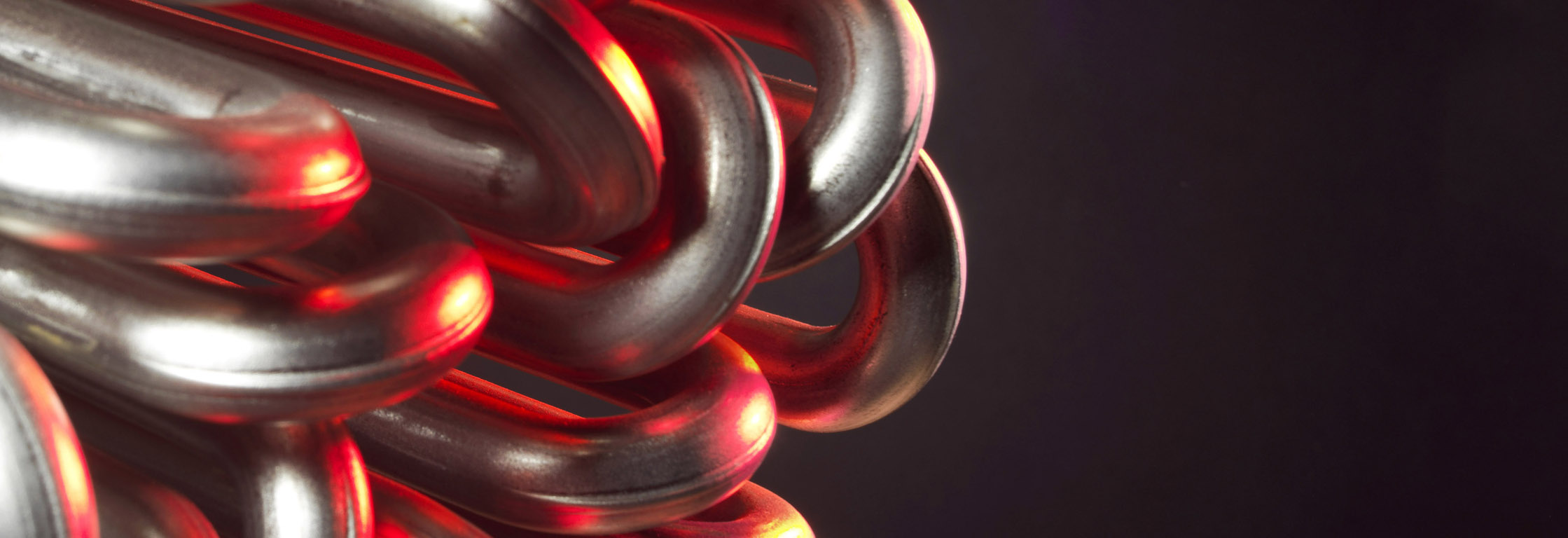

High-flux flange immersion heaters
Smaller equipment
Less space, weight, heat loss, cost saving, reduced thermal inertia

Increased productivity
More heat in less time for shorter production cycles
High temperature
Longer heater life in extreme conditions, very high temperatures
Product overview
- Customized product
- Wire Ni-Cr 80/20
- W/cm² : 10 à 200 W/cm²
- Voltage: 24 V /48 V (DC), usually 110 to 750 V AC/DC, max medium voltage
- Operational temperature: from -270 °C to +1000 °C
- Pressure: up to 300 bars, higher on request
Advantages
- Temperature gradient improved by 10 compared to Magnesia
- Heating 100% homogeneous (Straight wire)
- Ring-shaped flow improves heat transfer up to 100 W/cm² and more
- Available in ATEX/IECEx
- Medium voltage
- No leakage current at high temperature
- Specific tube sheath to increase heat transfer coefficient and heat surface
- Reduced heater weight
Water
- Stagnant water, max load 8-12 W/cm², material: copper, 321, 316L
- Circulating water, max load 10-16 W/cm², material: copper, 316L, inc 800, inc 825
- Boric water, max load 8 W/cm², material: 316L
- Boiler water, max load 8-16W/cm², material: 316L, inc 800, inc 825
- Chlorated water, max load 6 W/cm², material: inc 825
- Sea water, max load 3.5-6 W/cm², material: inc 825, inc600
- Demineralized water / deionized / distilled / Softened,max load 4-6 W/cm², material: 316L, inc 800, inc 825
- Domestic hot water, max load 4-8 W/cm², material: copper, 316L, inc 825
- Caustic water (2%, 10%, <30%, 70%), max load 2.3-7W/cm², material: 316L, inc 825, inc 600
Oil
- Machine oil SAE 10, 30, 40 & 50, max load 2.0-3.5 W/cm², material: 316L
- Mineral oil , max load 0.5-3.5 W/cm² acc to temp, material: 321, 316L
- Lube oil, max load 2.3 W/cm², material: 321, 316L
Acid & corrosive fluid
- Acetic acid, max load 6W/cm², material: 316L, inc 825
- Boric acid, max load 6W/cm², material: inc 825
- Chloric, hydrofluoric, nitric, sulphuric acid, max load 1.5W/cm², material: teflon coat
- Boric acid, max load 6W/cm², material: inc 825
- Alkaline bath, max load 6W/cm², material: 321 (no corrosive compound), 316L
- Phosphate bath, max load 4W/cm², material: 316L,inc 825
Glycol
- Ethylene glycol,Propylene glycol, 4 to 8 W/cm² acc to concentration, material: 321, 316L
Others
- Asphalt, tar, and other heavy or highly viscous compounds, max load 0.5 -1.5W/cm², material: 316L
- Milk, max load 0.3W/cm², material: 316L
Gas
- Air, max load 0.1 -8W/cm² acc. to sheath temp., material: 321
- Circulating air, max load 0.1 -8 W/cm² acc. to sheath temp., material: 309
- Natural gas, max load 0.1 -8 W/cm² acc. to sheath temp., material: 321, 316L
- Argon, nitrogen, W/cm² acc. to sheath temp., material: 321, 316L, inc 825, inc 600
- Propan, butane, W/cm² acc. to sheath temp., material: 321, 316L
- Oxygen, hydrogen, W/cm² acc. to sheath temp., material: 316L
Solids
- Mass of steel or stainless steel (bolt)
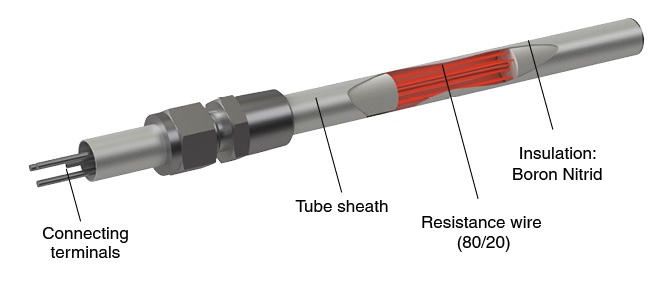
Technical description
- Heating element tube diameter according to application:
- High flux heating element : 8.5, 16, 19 mm
- Bolt heater: 10.7, 11.7, 12.2,15.7, 17.7, 19.7, 21.6, 24.6, 29.6 mm
- Tube material: Inox (321, 316L, 309), Incoloy 800 et 825, Inconel 600
- Wire Ni-Cr 80/20 (Max 1100°C on wire)
- Straight shape: possibility to bend only in cold part, max angle 90°
- Electrical connections on the same side 1Ph or 3 Ph.
- Enable to have circular heat exchange in case of circulation heater
- Temperature control can be done by a removable thermocouple in a sleeve located in the heart of the heater.
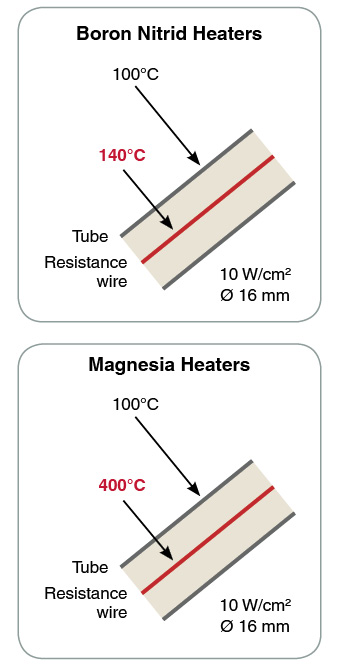
- High conductivity of boron nitrid (temperature gradient from 4 to 5°C) between wire and tube
- Corrugation possible (tube thickness ~2 mm) , heat exchange surface increased/speed (Re and Prandtl number)

Smaller equipment
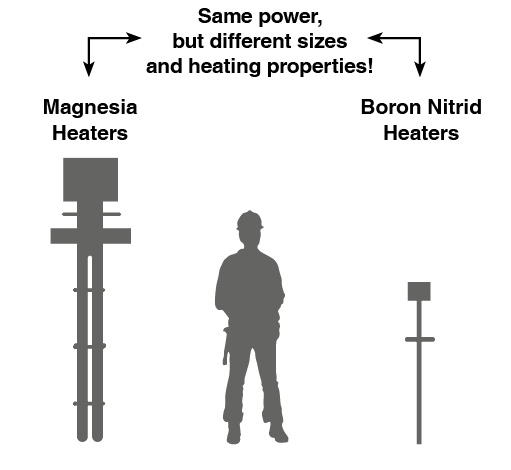
- Complete system cost reduction (especially when vessel with high pressure (DESP), insulation)
- Space saving and easier to handle
- Weight saving
- Temperature loss reduction (surface minimized)
- Easier handling for installation
- Inertia reduced, better temperature control accuracy
Liquid heating
Improved heat transfer (up to 100W/cm²) thanks to ring-shaped vessel to reduce the size of the heating system: corrosive, polluting or thermal fluid heating / high power pressure system / high power system / Steam super heater
Braking resistors
Circulation heater for offshore platforms
Flange immersion heaters
Reduce the size of highpower flange immersion heaters while ensuring good heat transfer. For tank heating.

Increased productivity
- More heat in less time for shorter production cycles
Bolt Heaters

Bring a lot of heat in the drilled bolt to reduce the maintenance cycle time (tightening and untightening of the nut.)
Matrix Heating
Bring a lot of heat in the matrix to reduce the cycle time in comparison to usual cartridges
Mold Heating
Bring a lot of heat in the mold for specific thermoforming process (Aeronautics, Automobile) to reduce the process cycle time
Ignition point
Ignition of inflammable gas using small equipment
High temperature
- High temperature process, up to 1000°C
- Temperature gradient improved by 10 compared to Magnesia
Gas heating
Heat process requiring high temperature such as bench tests with high air flow (aeronautics …) / chemical processes (Polymerization)




